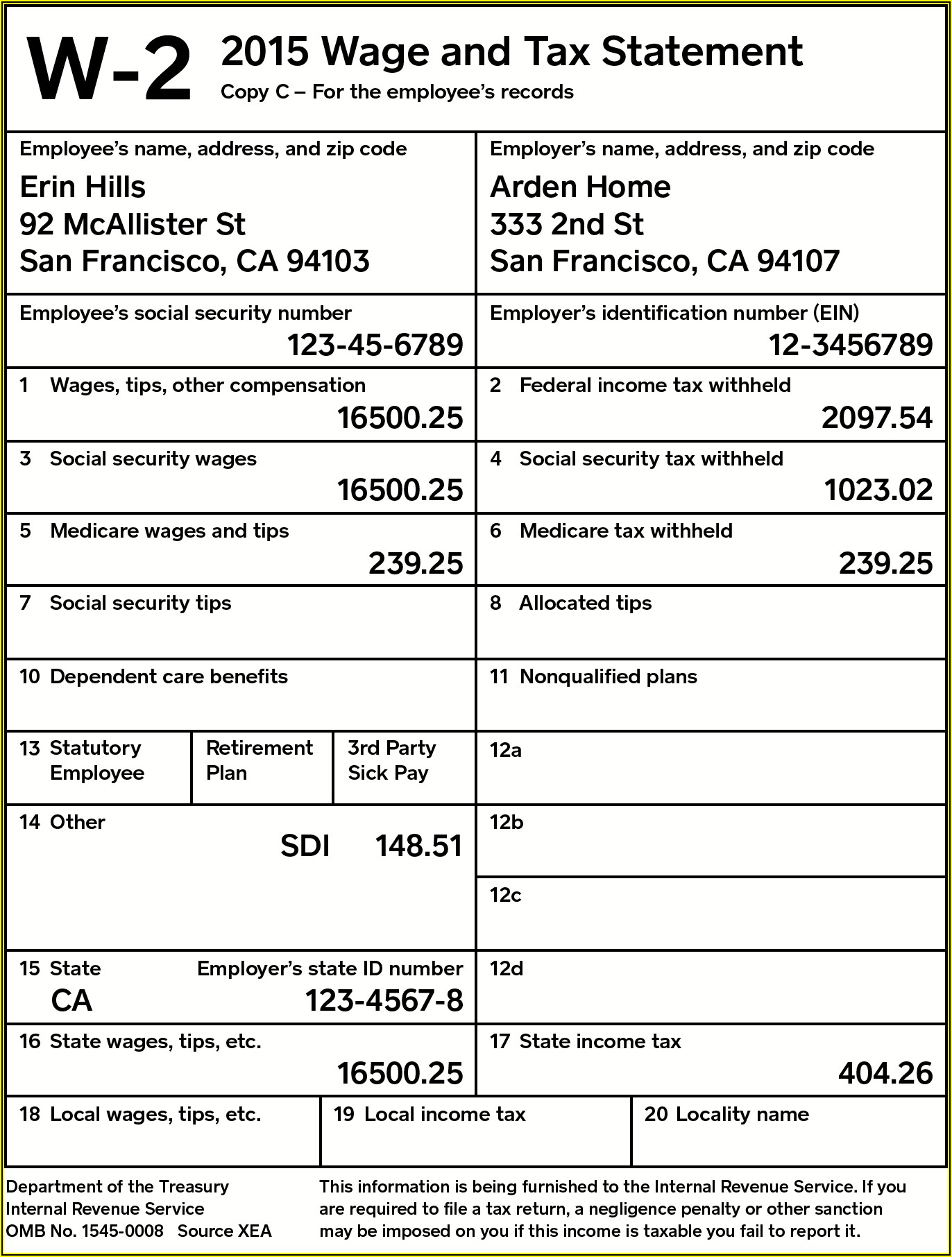
New York State Income Tax, often abbreviated as NYS Income Tax, is one of the most critical financial obligations for residents of the Empire State. Whether you're a long-time resident or a newcomer, understanding the intricacies of this tax system is essential for financial planning and compliance. With varying tax brackets, credits, and deductions, the NYS income tax framework can be both complex and rewarding. In this guide, we’ll dive deep into the specifics of NYS income tax, exploring its structure, implications, and how you can maximize your financial benefits while staying compliant.
From understanding how your income is taxed to learning about credits that could reduce your tax burden, this article aims to demystify the complexities surrounding NYS income tax. We’ll also address common questions like “What are the current tax rates?” and “How does NYS income tax compare to federal taxes?” With this information, you’ll be better equipped to navigate tax season with confidence.
As one of the largest revenue sources for New York State, income tax plays a pivotal role in funding public services such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure. By gaining a clear understanding of how NYS income tax works, you’ll not only fulfill your civic duty but also discover ways to optimize your tax situation. Let’s get started by exploring the essential aspects of this critical financial obligation.
Read also:Unveiling The Magic Of Retro Dti A Nostalgic Journey To The Past
Table of Contents
- What is NYS Income Tax?
- How Are Tax Brackets Determined in New York State?
- What Credits Can Reduce Your Tax Burden?
- Common Deductions You Should Know About
- How Does NYS Income Tax Compare to Federal Taxes?
- What Are the Consequences of Non-Compliance?
- How to File Your NYS Income Tax?
- FAQs About NYS Income Tax
What is NYS Income Tax?
New York State Income Tax, commonly referred to as NYS income tax, is a tax levied on the earnings of individuals and businesses residing or operating within the state. This tax is progressive, meaning that the rate increases as your income rises. The revenue generated from NYS income tax is used to fund essential public services, including schools, healthcare facilities, and transportation infrastructure.
Unlike federal income tax, which is uniform across the United States, NYS income tax is specific to New York State. It operates on a system of tax brackets, where different portions of your income are taxed at varying rates. For example, someone earning $50,000 annually will pay a lower percentage of their income in taxes compared to someone earning $200,000. This structure ensures that those with higher incomes contribute a fairer share to the state’s revenue.
Understanding NYS income tax is not only important for compliance but also for financial planning. By knowing how much of your income is taxed and what deductions or credits you qualify for, you can make informed decisions about savings, investments, and other financial matters. Additionally, failing to pay your NYS income tax can result in penalties, interest, and even legal consequences, making it crucial to stay informed and proactive.
How Are Tax Brackets Determined in New York State?
New York State utilizes a tiered tax bracket system to determine how much income tax residents owe. These brackets are adjusted periodically to account for inflation and changes in state policies. For the 2023 tax year, NYS income tax rates range from 4% to 8.82%, depending on your filing status and taxable income.
Single Filers
For single filers, the tax brackets are as follows:
- 4% on income up to $8,500
- 4.5% on income between $8,501 and $11,700
- 5.25% on income between $11,701 and $13,900
- 5.9% on income between $13,901 and $21,400
- 6.33% on income between $21,401 and $80,650
- 6.85% on income between $80,651 and $215,400
- 8.82% on income exceeding $215,400
Married Filing Jointly
For married couples filing jointly, the brackets are slightly higher:
Read also:Did Moonpie Starbox Die In Real Life Unveiling The Truth Behind The Online Persona
- 4% on income up to $17,150
- 4.5% on income between $17,151 and $23,600
- 5.25% on income between $23,601 and $27,900
- 5.9% on income between $27,901 and $43,000
- 6.33% on income between $43,001 and $161,550
- 6.85% on income between $161,551 and $323,200
- 8.82% on income exceeding $323,200
Why Are Tax Brackets Important?
Tax brackets are crucial because they determine the amount of tax you owe based on your income level. Understanding which bracket you fall into can help you plan your finances more effectively. For instance, if you’re close to moving into a higher tax bracket, you might consider strategies like increasing contributions to retirement accounts to reduce your taxable income.
What Credits Can Reduce Your Tax Burden?
One of the most effective ways to lower your NYS income tax liability is by taking advantage of available tax credits. These credits directly reduce the amount of tax you owe, making them more valuable than deductions, which only reduce your taxable income. Below are some of the most common credits available to New York State residents.
Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)
The Earned Income Tax Credit is a refundable credit designed to assist low- to moderate-income working individuals and families. To qualify, you must meet specific income requirements and have earned income from employment or self-employment. The amount of the credit depends on your income, filing status, and the number of qualifying children you have.
Child and Dependent Care Credit
This credit is available to taxpayers who pay for childcare or care for a dependent so they can work or look for work. The credit amount varies based on your income and the expenses incurred for care. It’s particularly beneficial for working parents who rely on daycare services or after-school programs.
Are There Other Credits Worth Exploring?
Yes, New York State offers several other credits, including the College Tuition Credit, the Real Property Tax Credit, and the Empire State Child Credit. Each of these credits has specific eligibility requirements and can significantly reduce your tax burden if you qualify. It’s worth consulting a tax professional or using tax preparation software to ensure you’re claiming all the credits available to you.
Common Deductions You Should Know About
In addition to tax credits, deductions are another powerful tool for reducing your NYS income tax liability. Deductions lower your taxable income, which in turn reduces the amount of tax you owe. Here are some of the most common deductions available to New York State residents.
Standard Deduction
The standard deduction is a fixed amount that reduces your taxable income. For the 2023 tax year, the standard deduction for single filers is $8,000, while married couples filing jointly can claim a standard deduction of $16,050. If your itemized deductions exceed these amounts, you may benefit from itemizing instead.
Itemized Deductions
Itemized deductions include expenses such as mortgage interest, medical expenses, and charitable contributions. To itemize, you’ll need to keep detailed records of these expenses throughout the year. While itemizing can be more time-consuming, it can result in significant tax savings if your total deductions exceed the standard deduction.
How Do Deductions Impact Your NYS Income Tax?
Deductions are essential because they directly lower your taxable income, which can place you in a lower tax bracket. For example, if your taxable income is $50,000 and you claim $10,000 in deductions, you’ll only be taxed on $40,000. This can result in substantial savings, especially if you’re on the cusp of moving into a higher tax bracket.
How Does NYS Income Tax Compare to Federal Taxes?
Understanding the differences between NYS income tax and federal income tax is crucial for effective tax planning. While both taxes are based on your income, they operate under different rules and rates. Federal income tax rates range from 10% to 37%, depending on your income and filing status, which is generally higher than NYS income tax rates.
One key difference is that federal taxes are uniform across the country, while NYS income tax is specific to New York State. Additionally, federal taxes offer a broader range of deductions and credits, such as the Student Loan Interest Deduction and the American Opportunity Credit, which may not be available at the state level.
What Are the Key Similarities?
Despite their differences, NYS income tax and federal taxes share some similarities. Both systems use a progressive tax structure, where higher incomes are taxed at higher rates. Additionally, both taxes allow for deductions and credits, although the specifics vary between the two systems.
What Are the Consequences of Non-Compliance?
Failing to comply with NYS income tax requirements can result in serious consequences, including penalties, interest, and legal action. The New York State Department of Taxation and Finance is diligent in pursuing unpaid taxes, and non-compliance can lead to wage garnishment, liens on property, or even criminal charges in severe cases.
How Can You Avoid Penalties?
To avoid penalties, it’s essential to file your taxes accurately and on time. If you’re unable to pay your full tax liability by the deadline, consider setting up a payment plan with the state. Additionally, staying informed about changes to tax laws and seeking professional advice can help you remain compliant and avoid costly mistakes.
How to File Your NYS Income Tax?
Filing your NYS income tax is a straightforward process if you have the right information and tools. You can file electronically using the New York State Department of Taxation and Finance’s website or opt for paper filing if you prefer. Regardless of the method you choose, ensure that you have all necessary documents, such as your W-2s, 1099s, and receipts for deductions.
What Are the Filing Deadlines?
The deadline for filing NYS income tax is typically April 15th, aligning with the federal tax deadline. If you need more time, you can request an extension, but remember that this only extends the filing deadline, not the payment deadline. Any taxes owed must still be paid by the original due date to avoid penalties and interest.
FAQs About NYS Income Tax
What Happens If I Miss the Filing Deadline?
If you miss the filing deadline, you may incur penalties and interest on any unpaid taxes. The penalty for late filing is typically 5% of the unpaid tax for each month the return is late, up to a maximum of 25%. Additionally, interest accrues on the unpaid balance until it’s paid in full.
Can I Deduct My Federal Taxes from My NYS Income Tax?
No, you cannot deduct federal taxes from your NYS income tax. However, you can deduct certain state and local taxes from your federal tax return, subject to specific limitations.
How Do I Know If I Qualify for Tax Credits?
To determine if you qualify for tax credits, review the eligibility requirements for each credit on the New York State Department of Tax