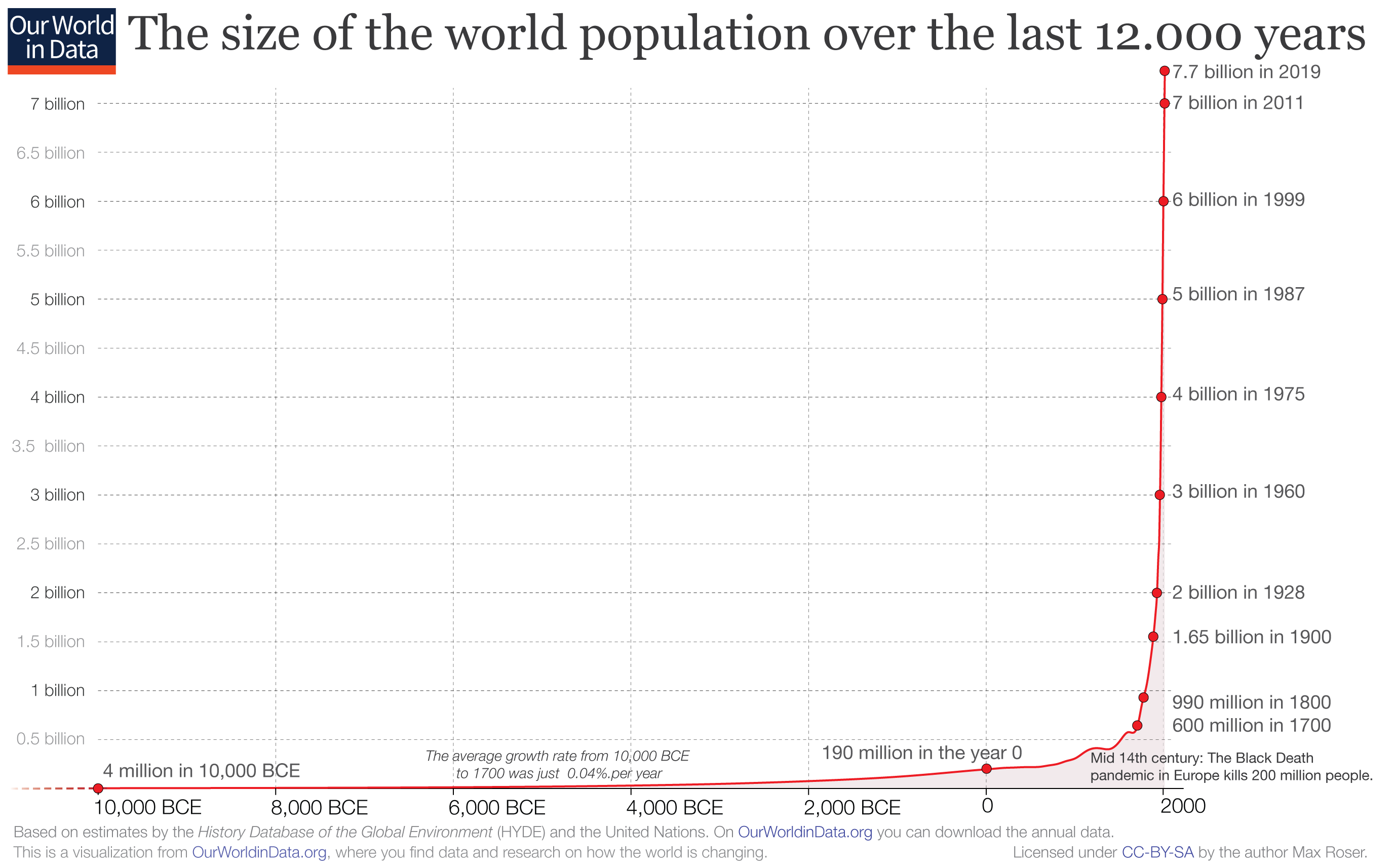
Global population growth has been one of the most significant phenomena shaping our world in recent centuries. With the global population surpassing 8 billion people in 2023, the pace of growth has raised questions about sustainability, resource allocation, and the future of humanity. The rapid expansion of human numbers has been driven by advancements in healthcare, agriculture, and technology, which have collectively reduced mortality rates and increased life expectancy. However, this growth has also brought challenges, such as environmental degradation, urban overcrowding, and economic inequality, making it a critical topic of discussion.
Understanding the dynamics of global population growth is essential for addressing its far-reaching consequences. The interplay between birth rates, death rates, and migration patterns has created a complex tapestry of demographic trends across different regions. While some countries are experiencing rapid population increases, others are grappling with aging populations and declining birth rates. This diversity in demographic trajectories underscores the need for tailored solutions that account for regional differences. As we delve deeper into this topic, we will explore how global population growth impacts economies, societies, and the environment.
The implications of global population growth extend beyond mere numbers. It influences everything from food security and water availability to climate change and geopolitical stability. As the world continues to urbanize and industrialize, the strain on natural resources is becoming increasingly apparent. Policymakers, researchers, and communities must work together to develop strategies that ensure sustainable development while accommodating the needs of a growing population. In the following sections, we will examine the causes, effects, and potential solutions to the challenges posed by global population growth.
Read also:Discover Skirby A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding And Embracing Skirby
Table of Contents
- What Are the Main Factors Driving Global Population Growth?
- How Does Global Population Growth Impact Resource Availability?
- What Are the Social Implications of Global Population Growth?
- Economic Consequences of Global Population Growth
- Environmental Challenges Posed by Global Population Growth
- Is Global Population Growth Sustainable in the Long Term?
- How Can We Address the Challenges of Global Population Growth?
- Future Projections and Scenarios for Global Population Growth
What Are the Main Factors Driving Global Population Growth?
Global population growth is influenced by a combination of biological, social, and economic factors. One of the primary drivers is the decline in mortality rates, particularly infant and child mortality. Advances in medical science, improved sanitation, and access to clean water have significantly reduced deaths caused by infectious diseases and malnutrition. This has led to a higher survival rate, contributing to population growth.
Another key factor is the increase in life expectancy. People are living longer due to better healthcare, nutrition, and living conditions. While this is a positive development, it also means that populations are growing older, which presents its own set of challenges. Additionally, fertility rates play a crucial role. In many developing countries, high fertility rates are driven by cultural norms, limited access to contraception, and economic factors that incentivize larger families.
Urbanization and Migration
Urbanization and migration are also significant contributors to global population growth. As people move from rural areas to cities in search of better opportunities, urban centers experience rapid population increases. This trend is particularly evident in developing countries, where urban populations are growing at an unprecedented rate. Migration, both internal and international, further amplifies population growth in certain regions.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements have indirectly fueled global population growth by improving agricultural productivity and food security. Innovations such as genetically modified crops, mechanized farming, and efficient irrigation systems have enabled farmers to produce more food to sustain larger populations. However, these advancements also raise concerns about environmental sustainability and equitable resource distribution.
How Does Global Population Growth Impact Resource Availability?
The relationship between global population growth and resource availability is complex and multifaceted. As the population expands, the demand for essential resources such as water, food, and energy increases exponentially. This heightened demand often leads to resource depletion, environmental degradation, and competition among nations and communities.
Water scarcity is one of the most pressing issues linked to global population growth. With more people relying on limited freshwater sources, many regions face severe shortages. Agriculture, which accounts for approximately 70% of global water usage, is particularly vulnerable to these shortages. This not only threatens food security but also exacerbates social and economic inequalities.
Read also:Who Is Drew Planten Unveiling The Life And Achievements Of A Remarkable Personality
Food Security Challenges
Global population growth poses significant challenges to food security. The need to feed a growing population has led to intensive farming practices, deforestation, and overfishing. These practices, while increasing food production in the short term, often result in long-term environmental damage. Soil degradation, loss of biodiversity, and climate change further complicate efforts to ensure sustainable food systems.
Energy Demand and Sustainability
The rising global population also drives up energy demand. Fossil fuels, which remain the primary source of energy for many countries, contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. Transitioning to renewable energy sources is essential for mitigating these effects, but the pace of adoption varies widely across regions. Addressing energy needs sustainably is a critical challenge in the context of global population growth.
What Are the Social Implications of Global Population Growth?
Global population growth has profound social implications, affecting everything from education and healthcare to employment and housing. As populations expand, governments and institutions face mounting pressure to provide adequate services and infrastructure. This can strain public resources and lead to disparities in access to essential services.
Education systems, for instance, must accommodate larger numbers of students, often with limited funding and facilities. This can result in overcrowded classrooms and reduced quality of education. Similarly, healthcare systems may struggle to meet the needs of growing populations, particularly in low-income countries where resources are already stretched thin.
Urbanization and Social Dynamics
Urbanization, driven by global population growth, transforms social dynamics in profound ways. Cities become melting pots of cultures, ideas, and innovation, but they also face challenges such as overcrowding, pollution, and crime. The rapid influx of people into urban areas can strain housing markets, leading to rising costs and inadequate living conditions for many.
Employment and Economic Opportunities
Employment is another critical area impacted by global population growth. While a larger workforce can drive economic growth, it also increases competition for jobs. In regions with high population growth, unemployment rates may rise, particularly among youth. This can lead to social unrest and exacerbate existing inequalities. Creating sufficient economic opportunities is essential for ensuring social stability in the face of global population growth.
Economic Consequences of Global Population Growth
The economic consequences of global population growth are both positive and negative. On the one hand, a growing population can stimulate economic growth by expanding the labor force and increasing consumer demand. This can lead to higher productivity, innovation, and economic diversification. On the other hand, rapid population growth can strain resources and infrastructure, leading to economic challenges.
In developing countries, population growth often outpaces economic development, resulting in poverty and inequality. Limited access to education, healthcare, and employment opportunities can trap individuals in cycles of deprivation. Addressing these disparities is crucial for ensuring that economic benefits are equitably distributed.
Impact on Global Markets
Global population growth influences global markets by shaping demand for goods and services. Industries such as agriculture, healthcare, and technology are particularly affected by demographic trends. For instance, an aging population may increase demand for healthcare services and retirement products, while a younger population may drive demand for education and consumer goods.
Regional Economic Disparities
Regional disparities in economic growth are often linked to population dynamics. Countries with high population growth rates may struggle to keep pace with infrastructure development and resource allocation. Conversely, countries with aging populations may face labor shortages and declining economic productivity. Bridging these disparities requires targeted policies and international cooperation.
Environmental Challenges Posed by Global Population Growth
Global population growth poses significant environmental challenges, including deforestation, pollution, and climate change. As more people require land, water, and energy, the pressure on natural ecosystems intensifies. This often results in habitat destruction, loss of biodiversity, and increased greenhouse gas emissions.
Deforestation, for example, is driven by the need for agricultural land and urban expansion. This not only threatens wildlife but also contributes to climate change by reducing the planet's capacity to absorb carbon dioxide. Similarly, pollution from industrial activities and waste generation poses health risks and damages ecosystems.
Climate Change and Global Population Growth
Climate change is closely linked to global population growth, as higher populations increase energy consumption and carbon emissions. Rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and sea-level rise disproportionately affect vulnerable populations, exacerbating existing inequalities. Addressing climate change requires global cooperation and sustainable practices to mitigate its impact on future generations.
Sustainable Solutions for Environmental Challenges
Implementing sustainable solutions is essential for addressing the environmental challenges posed by global population growth. Renewable energy, conservation efforts, and green technologies offer promising pathways for reducing environmental impact. Encouraging sustainable consumption patterns and promoting environmental awareness can also contribute to a more sustainable future.
Is Global Population Growth Sustainable in the Long Term?
The question of whether global population growth is sustainable in the long term is a topic of intense debate. While some argue that technological advancements and resource management can accommodate a growing population, others warn of the risks of overpopulation and resource depletion. Achieving sustainability requires balancing population growth with environmental, economic, and social considerations.
One approach to ensuring sustainability is through population stabilization. This involves promoting policies that encourage smaller family sizes, improving access to education and healthcare, and empowering women. By addressing the root causes of high fertility rates, countries can achieve more sustainable population growth trajectories.
Technological Innovations and Sustainability
Technological innovations play a crucial role in addressing the sustainability challenges of global population growth. Advances in renewable energy, precision agriculture, and water management offer solutions for reducing environmental impact. However, these innovations must be implemented equitably to ensure that all populations benefit from their advantages.
Global Cooperation for Sustainability
Global cooperation is essential for addressing the sustainability challenges posed by global population growth. International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement on climate change, demonstrate the potential for collective action. By working together, countries can share knowledge, resources, and strategies to create a more sustainable future for all.
How Can We Address the Challenges of Global Population Growth?
Addressing the challenges of global population growth requires a multifaceted approach that combines policy interventions, technological innovations, and community engagement. Governments, organizations, and individuals all have a role to play in ensuring that population growth is managed sustainably and equitably.
Policy interventions can include measures such as family planning programs, education initiatives, and economic incentives for smaller families. These policies aim to reduce fertility rates while improving quality of life. Additionally, investing in education and healthcare can empower individuals to make informed decisions about family size and resource use.
Community Engagement and Awareness
Community engagement is critical for addressing the challenges of global population growth. By raising awareness about the impacts of population growth and promoting sustainable practices, communities can take proactive steps to mitigate its effects. Grassroots initiatives, educational campaigns, and local partnerships can foster a sense of responsibility and collective action.
Role of Technology and Innovation
Technology and innovation are powerful tools for addressing the challenges of global population growth. From renewable energy solutions to smart city designs, technological advancements can help create more sustainable and resilient societies. Encouraging research and development in these areas is essential for finding practical solutions to complex problems.
Future Projections and Scenarios for Global Population Growth
Future projections for global population growth vary depending on demographic trends, policy interventions, and unforeseen events. According to the United Nations, the global population is expected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050 and 10.4 billion by 2100. However, these projections are subject to change based on factors such as fertility rates, mortality rates, and migration patterns.
Scenarios for global population growth range from optimistic to pessimistic. In the best-case scenario, population growth